5-minute read - by Kate Brunton, October 20, 2022
Antoine Kempen's materials science expertise has come in handy many times over the course of his 14-year career at ASML. Since joining the company in 2008 as a system engineer, Antoine has made significant contributions to EUV (extreme ultraviolet) lithography source optics and tin management and to DUV (deep ultraviolet) wafer table lifetime. He currently holds 16 US patents across 25 ASML patent families.
Unsung heroes
Chemistry and materials science are perhaps lesser-known fields of expertise at ASML, even though they’re important to the semiconductor industry in general. “ASML is by tradition about mechanics, mechatronics, physics and optics,” says Antoine. “That’s where the heart of the company is – but in order to make all that, you need materials, and thus knowledge of chemistry and materials science.”
Antoine notes that chemistry and materials science are sometimes seen as sources of problems rather than solutions. “And yes, they do occasionally cause problems,” he admits. “If you have an issue where a part wears out prematurely, you can say, ‘Well, the material is not good’. But they are also increasingly part of the solution. I'm proud to be the first fellow at ASML with a materials science background.”
Dutch grown
Antoine grew up on a dairy farm the heart of the Netherlands and went on to study materials science at TU Delft , completing his master’s degree in 1997. He earned his PhD in 2001 from the Max Planck Institute in Stuttgart, Germany, then came to Brainport Eindhoven where he worked for the Netherlands Organization for Applied Scientific Research (TNO) for seven years before joining ASML. He was named a Fellow in June 2022 at the annual ASML Technology Conference , the largest developer event in the world.
Fighting contamination and corrosion
Antoine has devoted much of his career at ASML to the cleanliness of our optics systems. EUV optics posed an exciting challenge for him, and he was met with “many surprises in the form of so many different contamination mechanisms.”

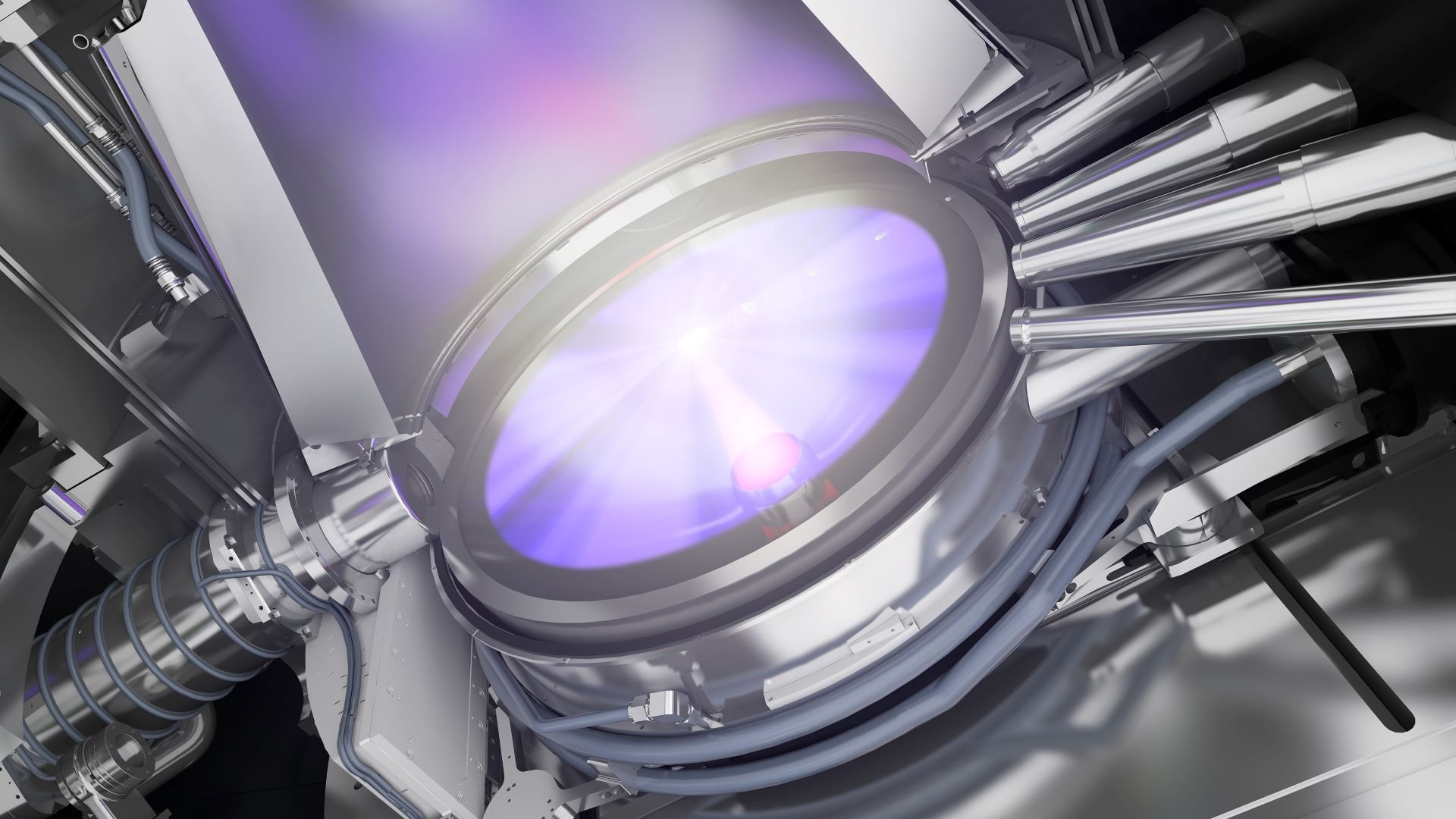
ASML’s lithography machines use ultraviolet light to ‘print’ patterns on silicon wafers that form the basis of a microchip. In our EUV machines, the light is generated in a special way: by firing laser pulses at droplets of tin to vaporize them into a plasma that emits EUV light.
The plasma can easily damage materials, though, and the optical components in lithography machines are extremely sensitive. For example, the component closest to the plasma is the collector mirror. Only a short distance and a bit of hydrogen gas separate the collector from the tin droplets being vaporized, and the collector can be ruined by just a few nanometers of contamination.
“We’ve been working on finding materials that are resistant to these circumstances,” says Antoine. “Liquid metals, including tin, are harmful toward almost all other materials, and in combination with hydrogen plasma they are virtually impossible to deal with.”
Antoine helped to create the specifications and requirements for EUV cleanliness to improve the lifetime of the optics. That, together with his work on tin management and collector lifetime for the 250 W EUV source, is what he considers to be his most important achievement at ASML. However, he admits that he finds that a bit difficult to say. “We all work in teams, so it’s often a group effort to arrive at solutions.”
Finding a loophole
In 2018 during the development of the 250 W EUV source, ASML ran into a big problem. “Every time after several hours of operation, the collector would start degrading extremely fast and no one could figure out why,” Antoine recalls. “It was a very big escalation. We could not solve it. We were in daily meetings with [ASML CTO] Martin van den Brink and a big team from across the ocean, and it was a high-stress situation for a lot of people.”

All aspects of the light source were considered as possible culprits: heating, plasma, mechatronics, gas flows, and more. Finally, after finding that the collector performed better under certain conditions, the team realized that it had been a chemistry problem all along.
Solving the problem meant reversing their design approach. Rather than searching for materials that would work under the conditions present in the light source, the team tweaked the source conditions to make them more compatible with the materials in the collector. Chemistry was no longer the cause of after-the-fact headaches – it played an important role in the system design.
“Antoine’s work was essential to understanding and modeling the physical phenomena behind the problem and to optimizing the source conditions,” said ASML head of System Engineering Jan van Vlerken during the Fellow award ceremony. “This led to an enormous improvement of the EUV source collector lifetime.”
A new DUV challenge
After this achievement Antoine felt it was time to move on to other things, so he turned his focus to coatings for DUV wafer tables. “Why DUV wafer tables? Well, it was one of the biggest challenges ASML was dealing with at the time, and given my background I thought I could help.”
The DUV wafer table was known to suffer from degradation. “When I arrived in the project, I found that there was one coating that was not really optimized for the use case,” says Antoine. “So I started making a roadmap. We had problems with wafer-table wear as well as corrosion, and I knew that both could be tackled by optimizing this coating – but only if we could make the coating specific enough for the problem.” He and the team developed corrosion- and wear-resistant coatings that achieved promising results. “These new coatings, together with the development of a service action that restores the coatings to their new state, really helped us to get out of the woods.”
“Antoine has been instrumental in finding and understanding the main degradation mechanisms caused by electrochemical wear and defining the corresponding solutions,” says his manager, René Oesterholt, “which ultimately improved the wafer table lifetime significantly."

Keeping it light
According to Antoine, humor is the antidote to stress. “I find it extremely important to keep things light,” he says. “We all experience pressure at work, but if you can keep yourself emotionally detached through a bit of humor, it frees the mind to come up with solutions faster.
“That’s what I like about this company,” he continues. “We work together as if we’re on a playground, but meanwhile doing serious stuff.”
Antoine advises his mentees to strive for work–life balance. “Spending too many hours a day working is not good for anybody. Especially if you're in a role where you need to be creative. You need to have time to process in the background, so having a hobby where you don't need to think is perfect.” Antoine’s preferred hobby is biking – “the most common hobby of, I think, everybody in the Netherlands.”
Chemistry and materials science play a role in many areas of ASML, including resist engineering, pellicle development, and contamination control. Want to join our team? View all chemistry and materials science jobs.